What is a Complex Gateway in BPMN and why it matters?

20-02-2024
11 min
The Complex Gateway is a special BPMN element used only in rare situations. Most Business Processes can be modeled with the standard Gateways:
- Exclusive (XOR) – choose one path
- Parallel (AND) – take all paths
- Inclusive (OR) – take some optional paths
However, sometimes you need behavior that is more flexible and more precise than these Gateways can provide. This is when the Complex Gateway becomes useful.
What is a Complex Gateway?

A Complex Gateway is a customizable Gateway that lets you define exactly when it should activate and which paths it should take. It is shown as a diamond with an asterisk (*).
Unlike other Gateways that follow fixed rules, the Complex Gateway uses expressions to decide:
- When to fire
- What to wait for
- Which paths to activate
This makes it powerful, but also harder to understand without extra explanation.
How the Complex Gateway works
The Complex Gateway relies on three main attributes:
| Parameter | Meaning | Example / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| activationCondition (activationExpression) | A rule (true/false) that tells the Gateway when to proceed | “Continue when at least 2 of 3 parallel Tasks are finished.” |
| activationCount | A live counter of how many incoming tokens arrived | You can reference this value inside the activation expression |
| waitingForStart | Flag showing the internal state of the Gateway | true → waiting to activate false → waiting to reset |
All these values are stored inside the gateway’s internal attributes - they are not visible on the BPMN diagram. Because of this, it’s a good idea to add a text annotation next to the Complex Gateway that explains the activation rule in plain language. This helps anyone reading the diagram quickly understand the logic without digging into technical details.
Two-Phase Behavior
The Complex Gateway always works in two steps:
Phase 1: Waiting for Start
The gateway monitors all incoming flows. When your activation rule becomes true, it:
- Takes all tokens currently waiting
- Checks outgoing conditions
- Sends tokens down all valid outgoing flows
- Remembers which incoming flows were used
- Switches to reset mode
Phase 2: Waiting for Reset
Now the gateway waits for the rest of the incoming flows (the ones that did not send a token earlier). Once they arrive - or are confirmed not to arrive - the gateway resets and is ready for the next cycle.
Branching (splitting the flow)
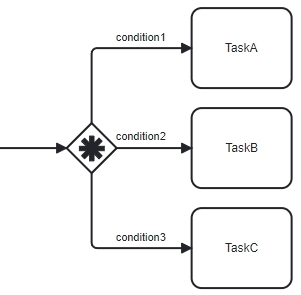
When used to split the flow, the Complex Gateway works just like an Inclusive Gateway:
- It checks each outgoing condition
- Sends tokens to all paths where the condition is true
Nothing special happens here.
Merging (joining the flow) - the real strength
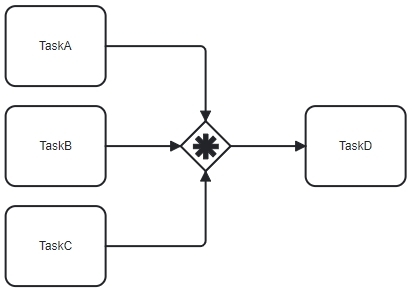
The real power of the Complex Gateway is on the incoming side. Here, you can define custom rules for when the process should continue.
Examples:
- “Go forward when the first Task finishes.”
- “Continue when 2 out of 3 Tasks are complete.”
- “If customer risk is high, wait for more approvals.”
This custom merging behavior is what makes the Complex Gateway irreplaceable in some situations.
Real-life scenarios where the Complex Gateway helps
Below are simple, real-life Business Process scenarios that illustrate how a Complex Gateway can be used.
Scenario 1: First-arrival wins (Discriminator Pattern)
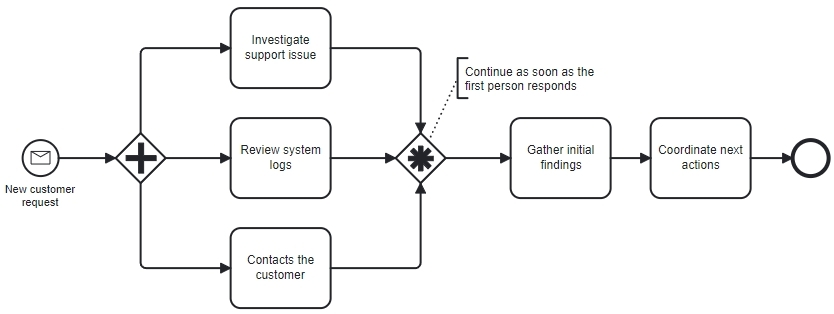
A customer submits a high-priority request. The system triggers three parallel actions:
- A support agent starts investigating
- A technical specialist reviews system logs
- A customer success manager contacts the customer
You want the Process to continue as soon as the first person responds, because that person will take ownership of the case.
Why a Complex Gateway?
- A Parallel Gateway would wait for all three responses.
- An Exclusive merge would trigger the next step multiple times if all three respond.
- With a Complex Gateway, the process moves forward as soon as any one response arrives, and all later responses are safely ignored.
Scenario 2: N-out-of-M join (2 out of 3 assessments)
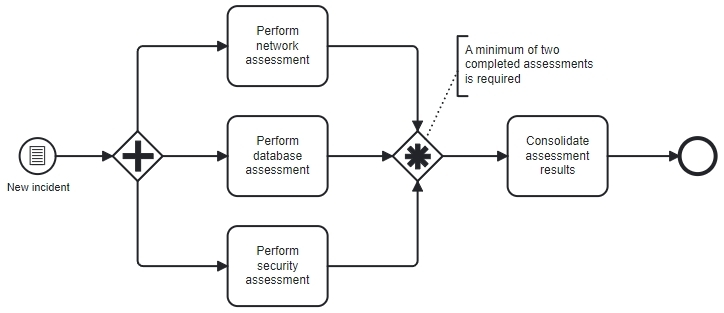
A new security incident is reported. As soon as it enters the incident-management system, the workflow launches three assessments in parallel:
- A network specialist performs a network vulnerability assessment
- A database engineer conducts a database integrity assessment
- A security analyst evaluates overall system security
Management wants the investigation to continue as soon as any two assessments are completed, because two independent confirmations are enough to proceed with consolidating the findings. The third assessment, if still running, becomes optional and does not delay the process.
Why a Complex Gateway?
- A Parallel Gateway would force the process to wait for all three assessments, even though only two are required.
- A simple Exclusive Gateway cannot count responses or enforce “2-out-of-3” logic.
- With a Complex Gateway, the process advances as soon as any two assessments finish, while the third (if still in progress) is safely ignored.
Scenario 3: Conditional Synchronization
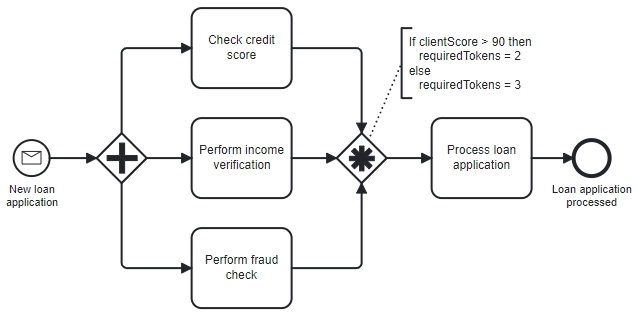
A bank processes a loan application with three parallel checks:
- Credit score check
- Income verification
- Fraud check
Normally, all checks are required.
But if the customer is a long-term client with a high reliability score, the bank may allow the process to continue once credit and income are available.
The rule might be:
- If clientScore > 90 → wait for 2 checks
- Else → wait for all 3 checks
Why a Complex Gateway?
It can evaluate both:
- The number of tokens waiting, and
- Customer data (clientScore)
This allows the Gateway to synchronize differently based on the context.
Workflow Patterns made simple
The BPMN specification says that the Complex Gateway can express several advanced workflow behaviors. Below is a simplified explanation.
Supported Patterns
| Pattern | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Structured Discriminator (WCP-9) | Continue after the first branch finishes |
| Blocking Discriminator (WCP-28) | Like the above, but block all other tokens until the Gateway resets |
| Structured Partial Join (WCP-30) | Continue after N out of M branches finish |
| Blocking Partial Join (WCP-31) | Same as N-of-M, but block extra tokens until reset |
In short: ➡️ The Complex Gateway can wait for any number of branches you choose, and it can ignore or absorb the rest.
When NOT to use a Complex Gateway
You should avoid the Complex Gateway when a simpler Gateway can do the job because:
- It is harder to understand by just looking at it
- It usually needs additional notes to explain the logic
- Some BPM tools don’t fully support it
- It can cause deadlocks if the condition never becomes true
Use it only when absolutely necessary.
Best Practices for Using a Complex Gateway
- Add text annotations - Explain when the gateway fires and what conditions apply.
- Keep expressions simple - Prefer clear rules like: activationCount ≥ 2
- Consider alternatives - Sometimes the same logic can be modeled Sub-Processes or a combination of XOR/AND/OR Gateways
Comparison with other Gateways
| Gateway Type | When It Fires | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Exclusive (XOR) | When one token arrives | Choose one path |
| Parallel (AND) | When all tokens arrive | Synchronize parallel Tasks |
| Inclusive (OR) | When all activated tokens arrive | Optional parallel paths |
| Complex | When your custom rule becomes true | Advanced merging, N-of-M joins, first-arrival wins |
Conclusion
The Complex Gateway fills an important gap in BPMN. It lets you define custom synchronization rules that standard gateways cannot express. This makes it perfect for:
- First-arrival wins
- N-out-of-M joins
- Conditional synchronization
- Dynamic business rules
However, this power comes with responsibility. Use the Complex Gateway only when simpler gateways cannot handle the scenario, and always document your rules clearly so that others can understand your model.
Used wisely, the Complex Gateway helps keep your process both flexible and accurate, while still remaining understandable to the people who maintain it.